Left-side chest pain can be a symptom of a heart problem, and therefore some people often think they're having a heart attack when it happens. However, pain on the left side of the chest can also indicate less serious issues, like excess intestinal gas, reflux, or anxiety attack.
When chest pain is intense and associated with symptoms like shortness of breath and tingling in the left arm, or doesn't improve within a few minutes, proceed to the hospital.
An electrocardiogram (ECG) will likely be ordered to detect cardiac problems, especially for older adults or people with chronic illnesses, like high blood pressure, diabetes, or high cholesterol.
6 Common Left Side Chest Pain Causes
Many health conditions can cause pain in the left part of the chest. They range from benign to potentially life-threatening. If you are in doubt about the potential causes of left-sided chest pain, seek emergency medical services immediately.
Treatment for chest pain depends on its causes. Learn about the most common causes of left-sided chest pain below and when to seek emergency help:
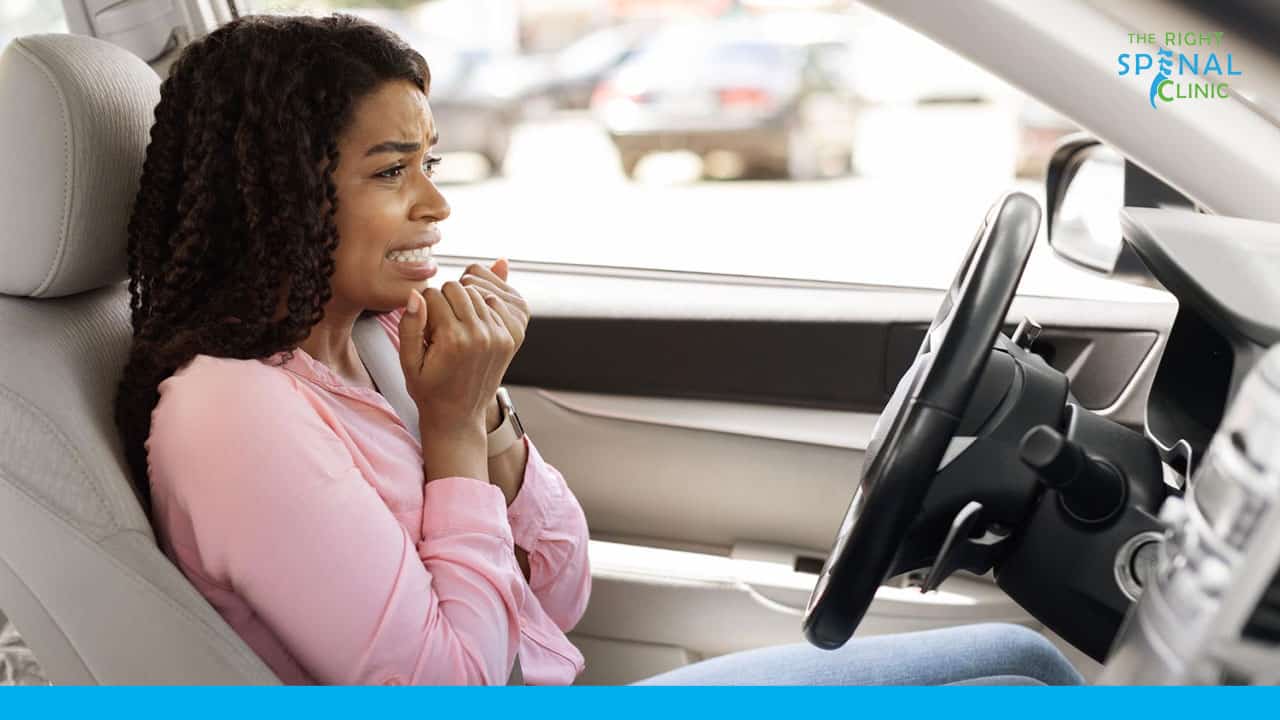
Panic Attack
Panic attacks come on suddenly and tend to peak within 10 minutes. Due to chest pain, tightness, and other symptoms, they can simulate a heart attack. Aside from chest pain, some other symptoms are the following:
- shortness of breath
- rapid heartbeat
- dizziness or shakiness
- sweating, hot flashes, or chills
- rapid breathing
- nausea
- feelings of unreality or detachment
- feeling as though you might choke
- intense fear or sense of doom
If you think you have an anxiety attack, seek immediate medical care. Other health issues, such as heart and thyroid disorders, can produce similar symptoms, so you want to be certain of the diagnosis.
How to ease a panic attack"
Panic disorder is a treatable mental health problem. Your doctor may recommend psychotherapy or cognitive behavioral therapy. If it’s an ongoing problem, some medications might help.
It might be helpful to:
- breathe deeply
- practice stress management and relaxation techniques
- join a support group
- avoid caffeine, tobacco, alcohol, and recreational drugs
- engage in regular physical activity
- get a full night’s sleep every night
Digestive Problems
Heartburn is the chest pain and discomfort you experience when stomach acid comes up into your esophagus (acid reflux or gastroesophageal reflux). You might also experience:
- a burning sensation in the upper abdomen and chest
- sour or metallic taste in your mouth
- stomach pushes contents to the back of your throat
Heartburn usually happens fairly soon after you’ve eaten. It can also occur when you lie down a few hours after eating. It can even wake you up from a sound sleep.
Acid reflux can progress to a more severe form called gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). The main symptom of GERD is frequent heartburn. Aside from chest pain, GERD can also cause coughing, wheezing, and trouble swallowing.
Treatment for heartburn"
You can generally ease heartburn with over-the-counter antacids. Your doctor can prescribe a stronger medication if necessary. If you have frequent heartburn, it might be helpful to:
It might be helpful to:
- eat smaller meals
- avoid fried and/or fatty foods
- eat slowly
- avoid alcohol and tobacco
- maintain a moderate weight
- don’t eat anything before bed
- avoid foods that may trigger you
Esophageal rupture
An esophageal rupture is a medical emergency that may cause non-cardiac chest pain. This condition occurs when the tube that connects the mouth to the stomach tears, allowing substances from the mouth to leak into the chest cavity and the lungs.
Sometimes, a person may experience this type of injury after excessive vomiting or experiencing physical trauma around the esophagus.

Angina
Angina is often a symptom of coronary heart disease, though other heart conditions may also cause it. Angina is the chest pain, heaviness, discomfort, or pressure you get when your heart muscle isn’t getting enough oxygen-rich blood.
The pain and discomfort usually include the left part of your whole body. You might also experience discomfort in your back.
The underlying condition must be properly diagnosed and treated. Diagnostic tests may include:
- blood testing
- electrocardiogram (ECG)
- stress test
- echocardiogram
- angiogram/cardiac catheterization
The treatment will depend on the cause and may include medication, lifestyle changes, and cardiac procedures as necessary.
Myocarditis
Myocarditis is an inflammation of the heart tissue, specifically the myocardium, the middle layer of the heart wall. Doctors often cannot identify the cause, but when they can, it is typically due to a viral infection.
Chest pain can be a sign that your heart muscle is inflamed. Other signs include:
- fatigue
- rapid or irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia)
- shortness of breath
Myocarditis can weaken your heart or cause permanent damage to the cardiac muscle. In some cases, a person can experience cardiac arrest or even death.
Mild cases may improve without treatment, but severe cases may require medication. Treatment depends on the cause.
Cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy is a disease of the cardiac muscle, which may lead to an enlarged heart. If you have cardiomyopathy, your heart can’t efficiently pump blood to the rest of your body.
It’s possible to have cardiomyopathy without any symptoms, but it can also cause chest pain. Other symptoms can include:
- difficulty breathing
- dizziness or fainting
- heart palpitations
- fatigue
- swelling of the ankles, feet, legs, hands, or abdomen
Treatment usually involves medications, cardiac procedures, and surgery. Certain lifestyle changes may help, too. These can include:
- reducing salt intake
- maintaining a moderate weight
- avoiding alcohol
- engaging in light to moderate exercise regularly

Heart Attack
A heart attack is a serious problem that requires immediate medical attention. This results when a blood clot reduces blood flow to the heart muscle. Some heart attacks begin with mild chest pain that slowly builds up. They can also start quite suddenly, with intense left chest pain. Other symptoms can include
- shortness of breath
- pain in your arm, shoulder, or neck
- nausea
- sweating
- lightheadedness or dizziness
- fatigue
- upper body pain
- trouble breathing
Heart attack symptoms in women
The symptoms depend from person to person. Both men and women can experience chest pain, gassiness or heartburn, difficulty breathing, or pain and discomfort in the shoulders, arms, neck, or jaw.
However, women are more likely to experience the following symptoms:
- shortness of breath
- nausea, vomiting
- pain in the upper back or jaw
- dizziness or lightheadedness
- extreme fatigue
If you experience these symptoms, seek medical attention immediately. With a heart attack, every second counts. The sooner you get treatment, the better the outcome will likely be.
A heart attack is a medical emergency that calls for immediate treatment.
When to Seek Emergency Help
Chest pain or heaviness, in general, is a concern for a heart attack or other life-threatening condition for which every minute matters. Call 911 or the local emergency services if you or someone near you has unexplained chest pain or sudden chest pain along with:
- chest tightness or heaviness
- chest pain
- severe pain on the left arm left side of the neck, left shoulder, and jaw
- breathing difficulties
- weakness, lightheadedness, or dizziness
- nausea or vomiting
How We Can Help
Looking for a primary care physician to check for your risks of a heart problem? Look no further!
The Right Spinal Clinic has a primary care physician who will always be available for any medical needs. Schedule an appointment by calling (813) 392 2164 or filling out our online appointment form.
Recent Posts











